Smas Superior Mesenteric Artery Syndrome
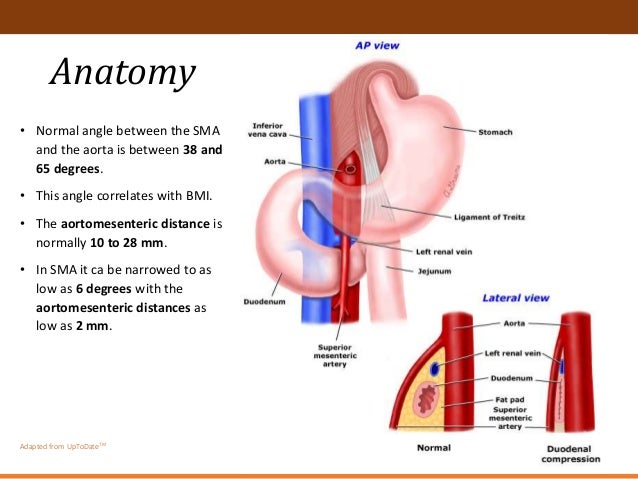
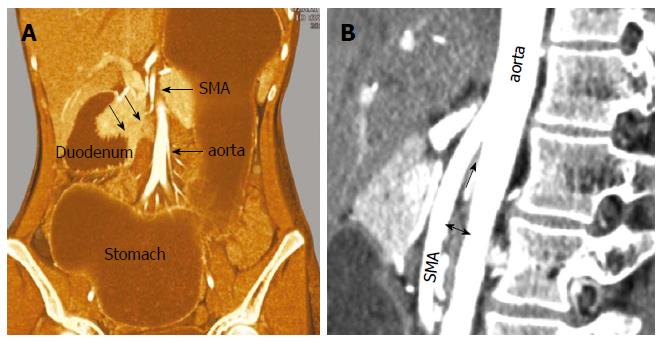
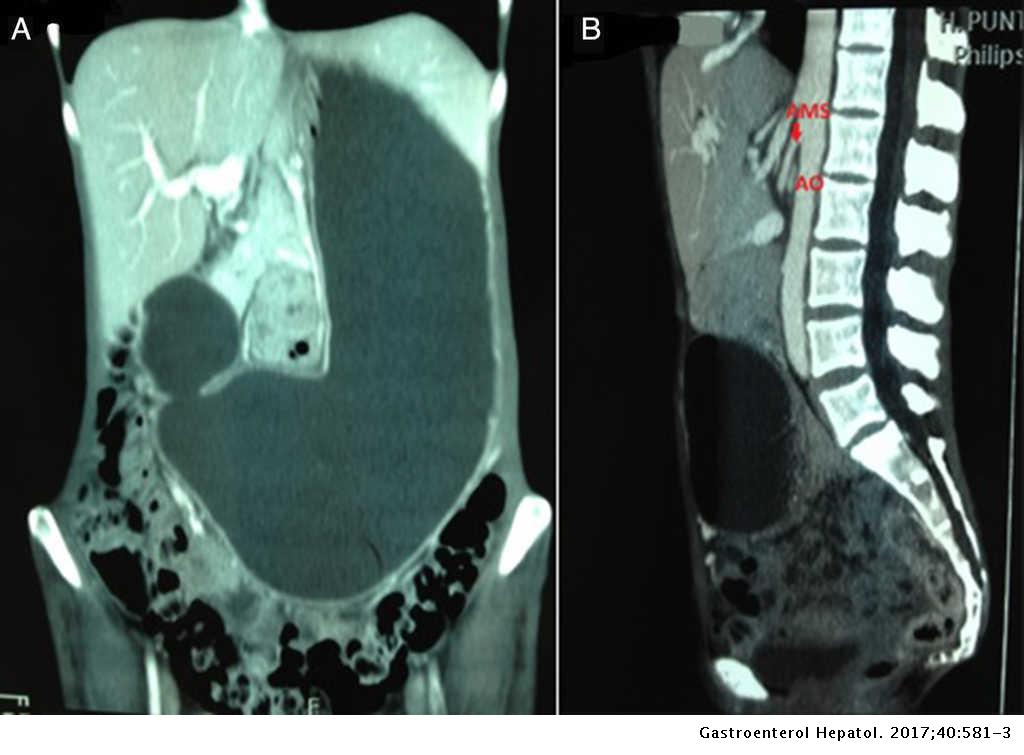
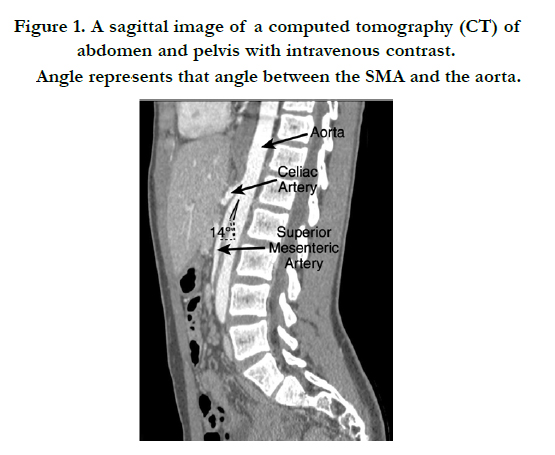
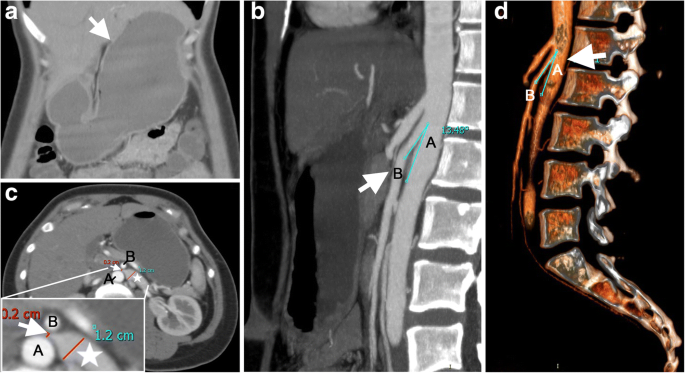
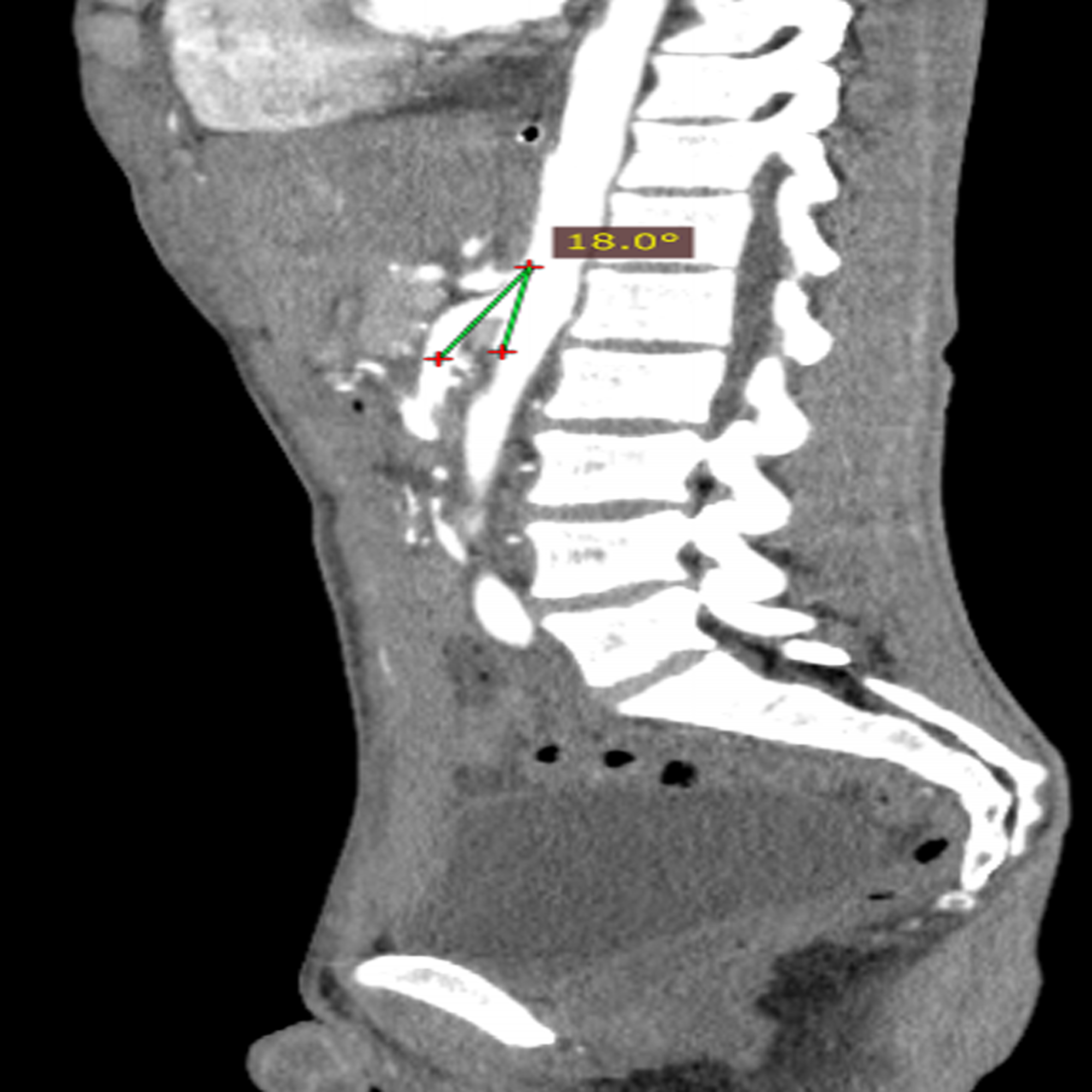
Smas superior mesenteric artery syndrome. Whatever the name this rare condition arises when the duodenum becomes compressed between the aorta and superior mesenteric artery. This compression causes partial or complete blockage of the duodenum. Superior mesenteric artery syndrome SMAS is an unusual condition where the third part of the duodenum is compressed between the superior mesenteric artery and the aorta.
In contrast to postoperative ileus bowel sounds are usually present in Superior Mesenteric Artery Syndrome SMAS. Superior mesenteric artery SMA syndrome also known as Wilkies syndrome and cast syndrome is a rare gastrointestinal disease that leads to obstruction of the duodenum. We are a registered 501c3 non-profit.
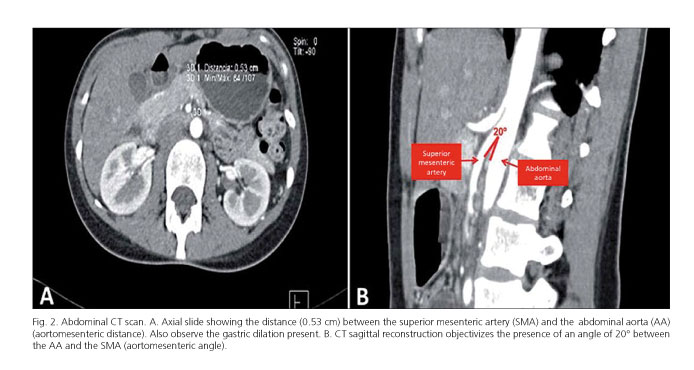
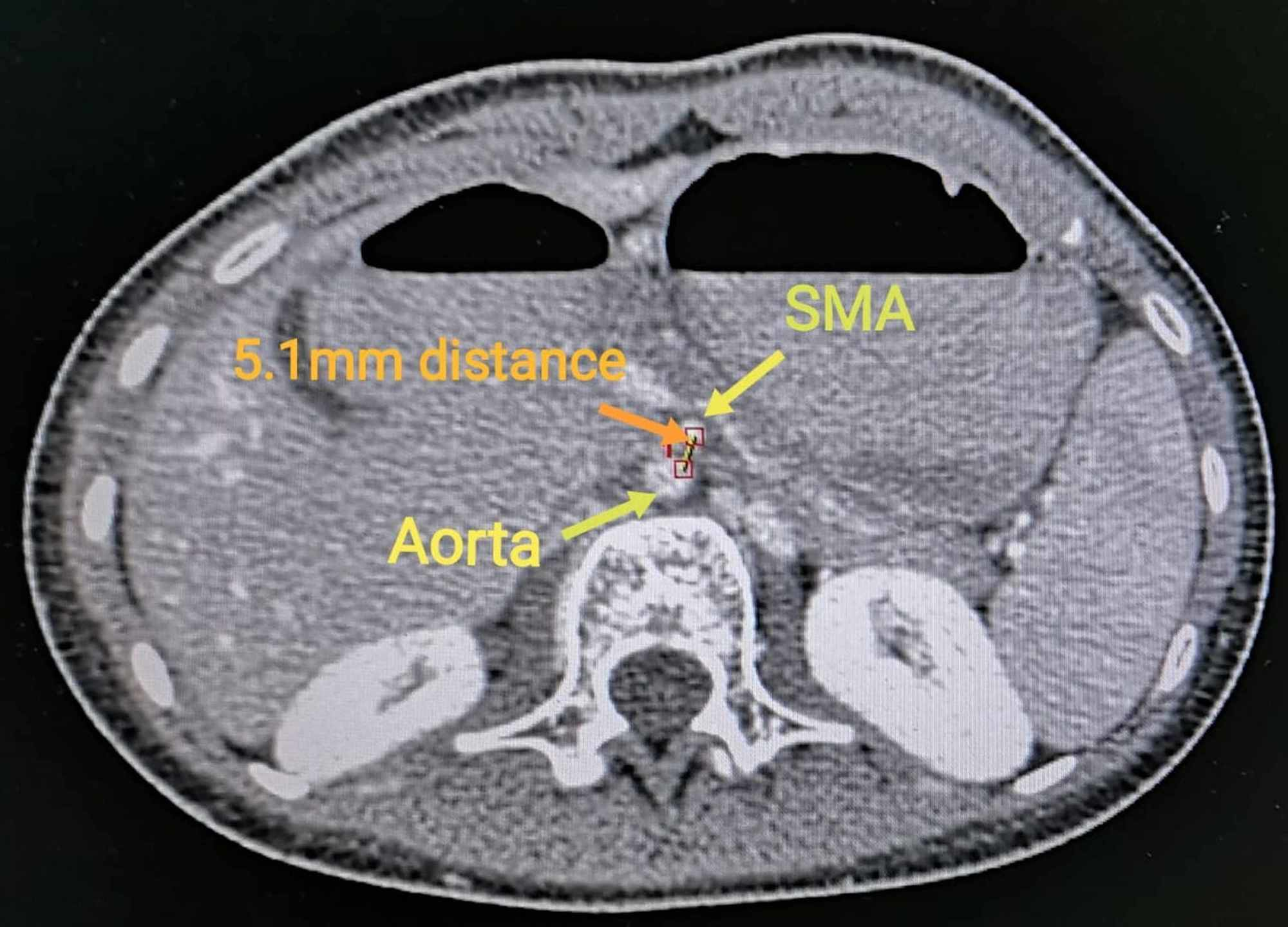
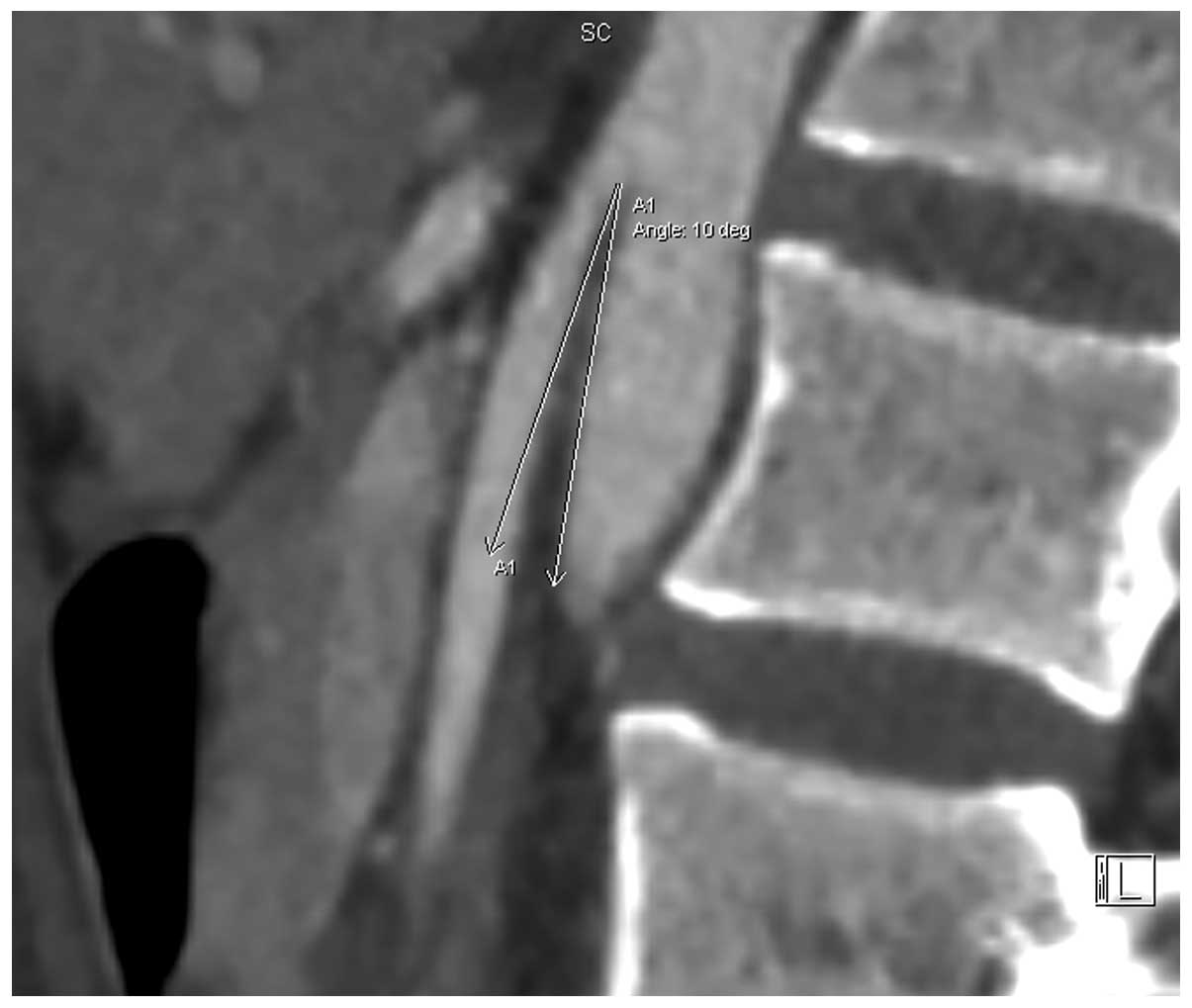
This compression causes partial or complete blockage of the duodenum. Superior mesenteric artery syndrome SMAS is a rare gastrointestinal disorder characterised by vascular compression of the third part of the duodenum in the angle between the superior mesenteric artery SMA and the abdominal aorta. SMA Syndrome may also be known by several other names including SMAS Wilkie Syndrome Cast Syndrome arteriomesenteric duodenal obstruction and chronic duodenal ileus.
It presents as an. Superior mesenteric artery syndrome is uncommon and characterized by postprandial epigastric pain nausea vomiting anorexia and weight loss. SMAS is a condition in which the third portion of the duodenum is squeezed between the superior mesenteric artery.
Superior Mesenteric Artery Syndrome SMAS Superior mesenteric artery syndrome SMAS is a digestive condition that occurs when the duodenum the first part of the small intestine is compressed between two arteries the aorta and the superior mesenteric artery. Superior mesenteric artery syndrome SMAS is a digestive condition that occurs when the duodenum the first part of the small intestine is compressed between two arteries the aorta and the superior mesenteric artery. Superior mesenteric artery SMA syndrome is a gastro - vascular disorder in which the third and final portion of the duodenum is compressed between the abdominal aorta AA and the overlying superior mesenteric artery.
Symptoms of persistent vomiting with abdominal distention epigastric tenderness and tympanic percussion note usually beginning 6 to 8 days after surgery or the application of a body casting but may occur up to 40 days thereafter. Superior mesenteric artery syndrome is a potentially life-threatening condition that affects the gastrointestinal tract. Congenital abnormalities weight-related conditions andor surgical procedures that result in alterations of the anatomy of the spine and surrounding structures including.
The compression causes partial to complete blockage in the duodenum therefore the patient can no longer eat and digest food. It occurs when the duodenum the part of the small intestine that connects to the stomach is compressed by a large artery in the abdomen.
In contrast to postoperative ileus bowel sounds are usually present in Superior Mesenteric Artery Syndrome SMAS.
Congenital abnormalities weight-related conditions andor surgical procedures that result in alterations of the anatomy of the spine and surrounding structures including. It occurs when the duodenum the part of the small intestine that connects to the stomach is compressed by a large artery in the abdomen. This compression causes partial or complete blockage of the duodenum. SMA Syndrome may also be known by several other names including SMAS Wilkie Syndrome Cast Syndrome arteriomesenteric duodenal obstruction and chronic duodenal ileus. SMASRAS stands for Superior Mesenteric Artery Syndrome Research Awareness and Support. The compression causes partial to complete blockage in the duodenum therefore the patient can no longer eat and digest food. Superior mesenteric artery syndrome SMAS is an unusual condition where the third part of the duodenum is compressed between the superior mesenteric artery and the aorta. Superior mesenteric artery syndrome SMAS is a rare gastrointestinal disorder characterised by vascular compression of the third part of the duodenum in the angle between the superior mesenteric artery SMA and the abdominal aorta. Superior mesenteric artery SMA syndrome is a gastro - vascular disorder in which the third and final portion of the duodenum is compressed between the abdominal aorta AA and the overlying superior mesenteric artery.
In contrast to postoperative ileus bowel sounds are usually present in Superior Mesenteric Artery Syndrome SMAS. Superior mesenteric artery syndrome SMAS is a digestive condition that occurs when the duodenum the first part of the small intestine is compressed between two arteries the aorta and the superior mesenteric artery. SMASRAS stands for Superior Mesenteric Artery Syndrome Research Awareness and Support. Symptoms of persistent vomiting with abdominal distention epigastric tenderness and tympanic percussion note usually beginning 6 to 8 days after surgery or the application of a body casting but may occur up to 40 days thereafter. Superior Mesenteric Artery Syndrome SMAS Superior mesenteric artery syndrome SMAS is a digestive condition that occurs when the duodenum the first part of the small intestine is compressed between two arteries the aorta and the superior mesenteric artery. The syndrome is caused by compression of the third part of the duodenum in the angle between the aorta and the superior mesenteric artery. Superior mesenteric artery syndrome is uncommon and characterized by postprandial epigastric pain nausea vomiting anorexia and weight loss.






































Post a Comment for "Smas Superior Mesenteric Artery Syndrome"