Chronic Lung Disease Of Prematurity
Chronic lung disease of prematurity. Obstructive spirometry with some acute bronchodilator reversibility is common after premature birth including in late preterm delivery. Diuretics and corticosteroids are effective in achieving short-term improvement in the status of ventilator dependent babies. Chronic pelvic inflammatory disease of the female pelvic organs andor tissues.
Chronic female pelvic abscess. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia BPD is a breathing disorder where an infants lungs become irritated and do not develop normally. 40 The Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children reported that children born at 3334weeks gestation had impaired childhood lung function comparable to children born 2532weeks and who required mechanical ventilation.
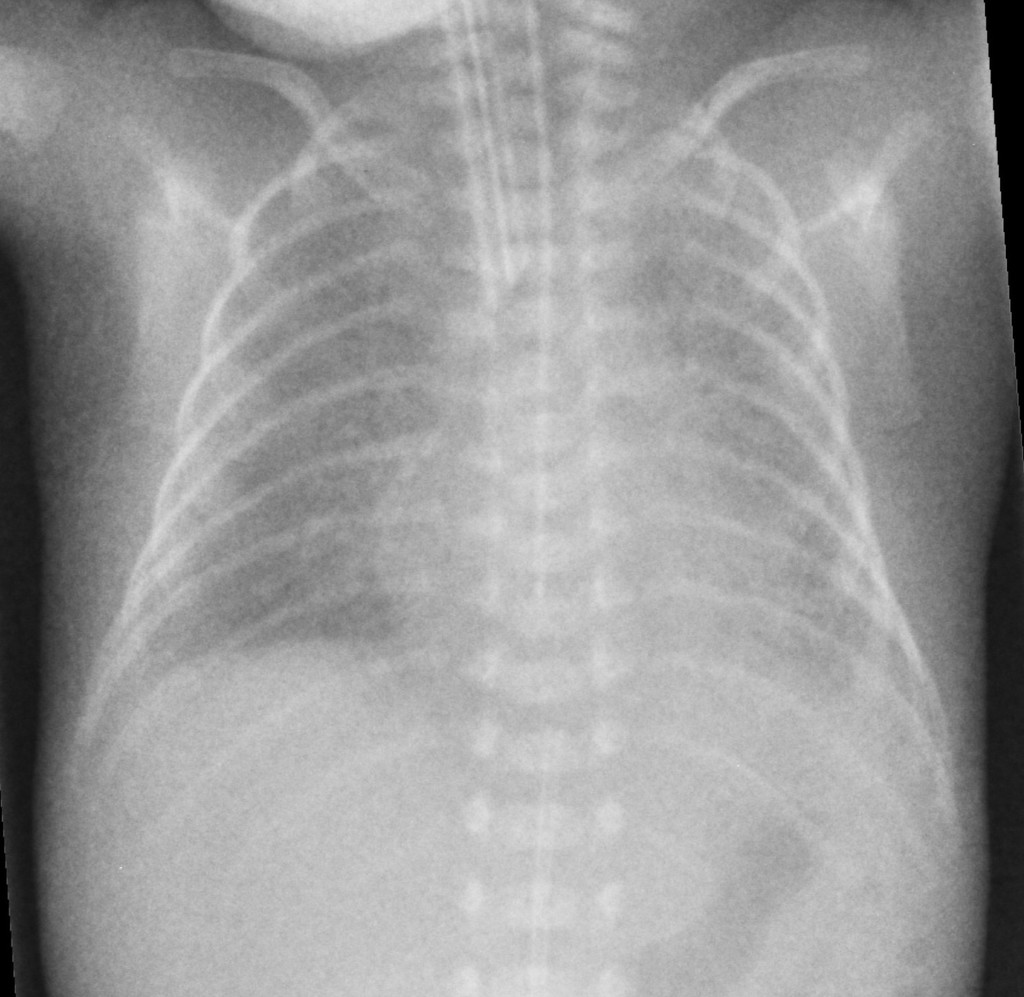
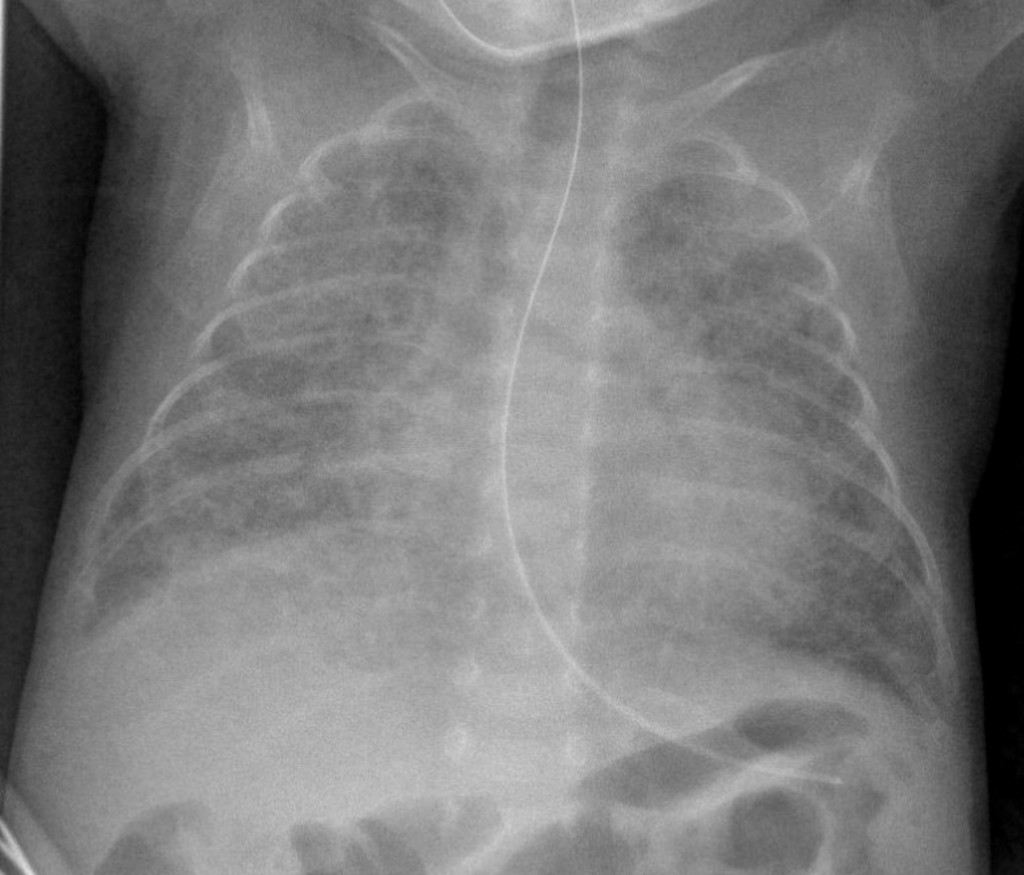
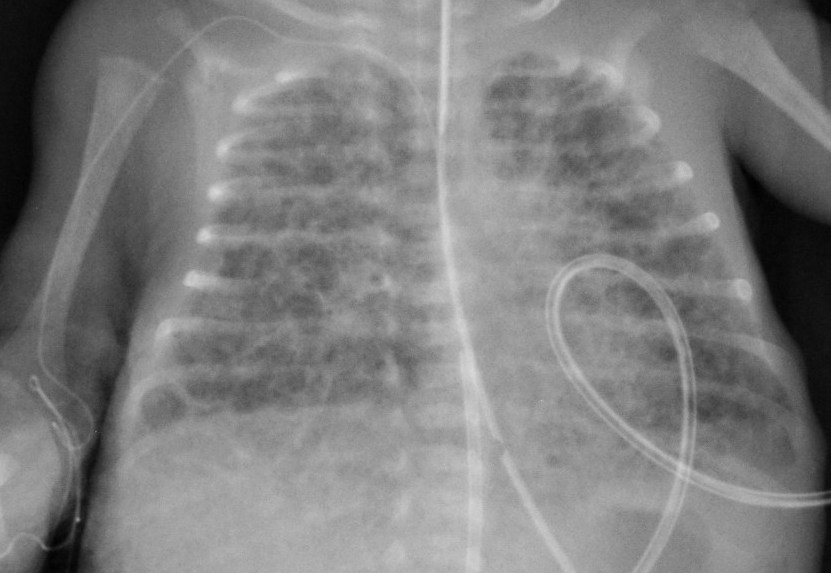
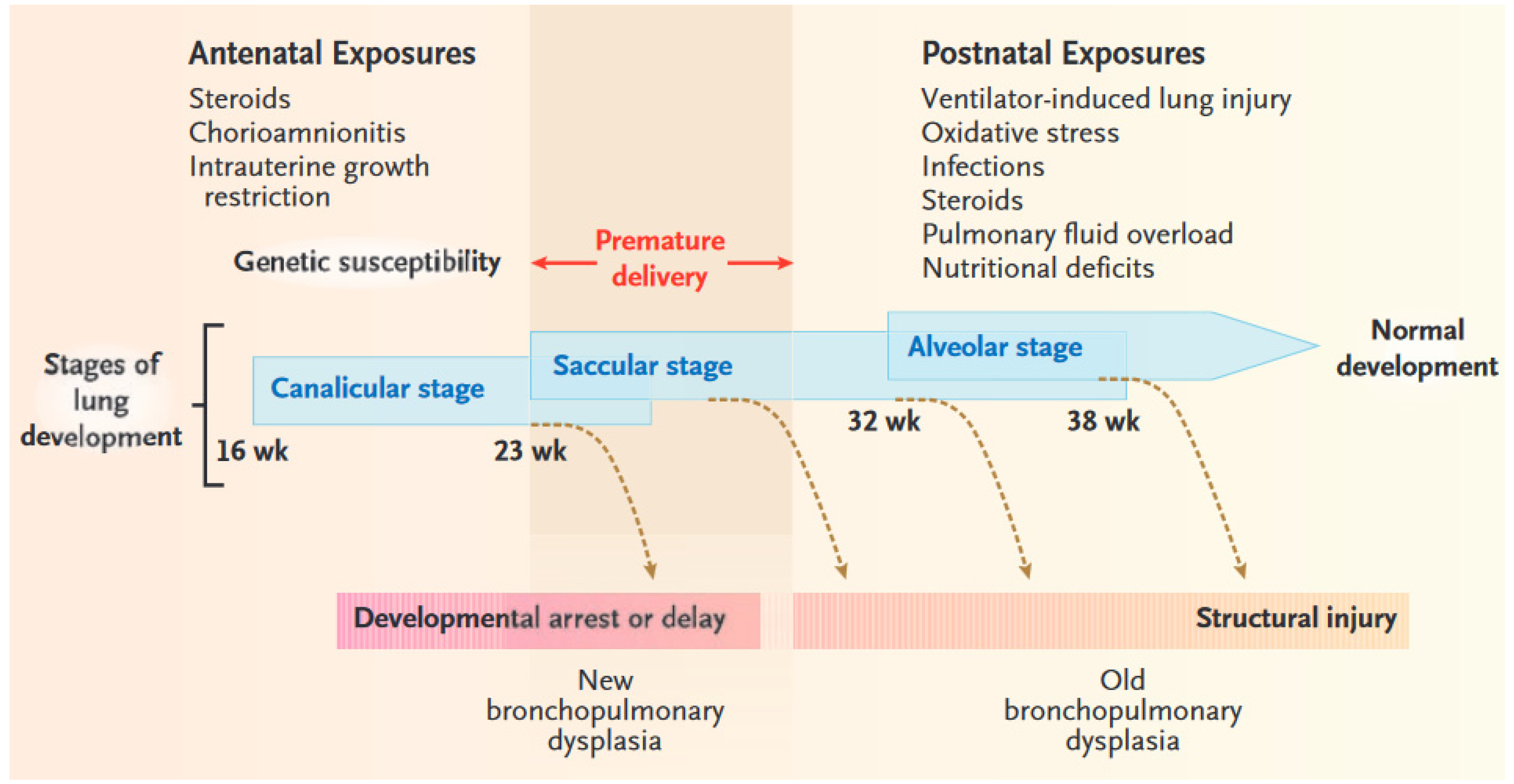
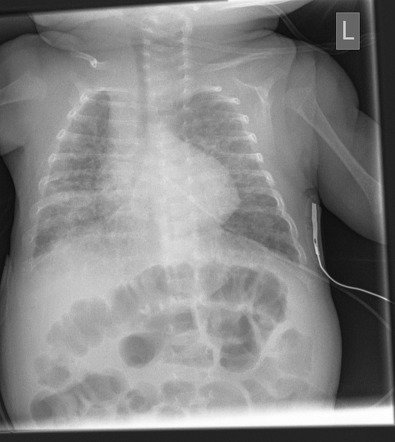
Most babies who now develop chronic lung disease have a birth weight below 1000 g and have only mild early respiratory disease requiring minimal ventilation and low concentrations of inspired oxygen. Advances in both perinatal and neonatal care over the past two decades have improved the survival of very preterm births but morbidity is significant among the survivors1 2 3 Chronic lung disease of prematurity CLD often also called bronchopulmonary dysplasia BPD is one of the most common sequelae in preterm births. Chronic lung disease of prematurity CLDP is also known as bronchopulmonary dysplasia.
Chronic female pelvic cellulitis. It occurs most often in low-weight infants born more than two months early. Chronic lung disease of prematurity CLD is commonly considered to be a consequence of assisted ventilation.
Chronic lung disease of prematurity. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia is also known as. Chronic respiratory morbidity is a common adverse outcome of preterm birth especially in infants who develop bronchopulmonary dysplasia BPD which is still a major cause of long-term lung dysfunction with a heavy burden on health care services and medical resources throughout.
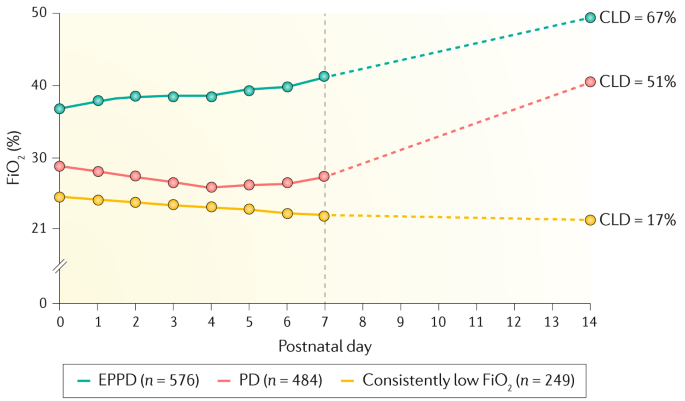
Chronic lung disease is defined as oxygen dependency at 36 weeks corrected gestational age. Since 1998 the management of CLD after discharge from neonatal unit follows national guidelines. It can occur when babies are born prematurely and need respiratory.
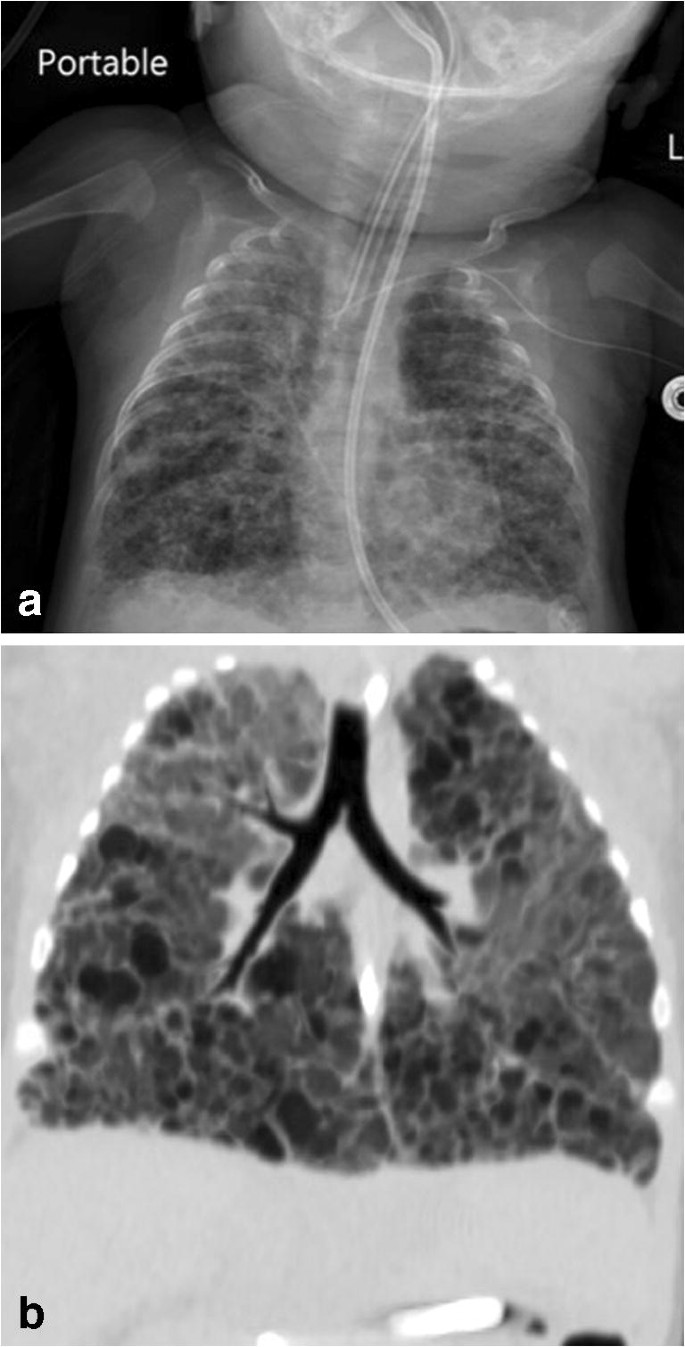
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia has become the most common chronic lung disease of infancy. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia brahn-ko-PUL-moh-nair-ee dis-PLAY-zhee-uh involves abnormal development of lung tissue.
Any condition in N730 specified as chronic.
Pelvic inflammatory disease chronic. However prior to the description in 1967 of bronchopulmonary dysplasia BPD following ventilator therapy for respiratory distress syndrome Wilson-Mikity syndrome WMS had been described in very preterm infants on minimal oxygen supplementation. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia is also known as. Most babies who now develop chronic lung disease have a birth weight below 1000 g and have only mild early respiratory disease requiring minimal ventilation and low concentrations of inspired oxygen. Its incidence varies from 10 to 60 in different regions of Chile. Chronic lung disease is defined as oxygen dependency at 36 weeks corrected gestational age. Diuretics and corticosteroids are effective in achieving short-term improvement in the status of ventilator dependent babies. Advances in both perinatal and neonatal care over the past two decades have improved the survival of very preterm births but morbidity is significant among the survivors1 2 3 Chronic lung disease of prematurity CLD often also called bronchopulmonary dysplasia BPD is one of the most common sequelae in preterm births. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia BPD is a chronic lung disease most commonly seen in premature infants who required mechanical ventilation and oxygen therapy for acute respiratory distress but can also occur in neonates that had a less severe respiratory course 13.
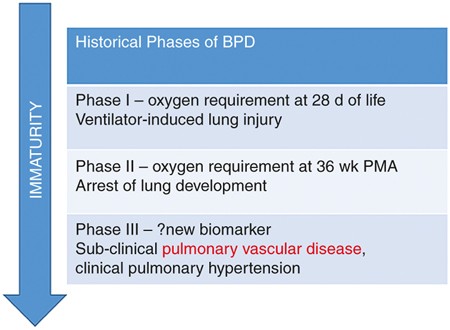
Most babies who now develop chronic lung disease have a birth weight below 1000 g and have only mild early respiratory disease requiring minimal ventilation and low concentrations of inspired oxygen. Day-to-day care is mostly directed towards improving symptoms with many common interventions. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia is a serious complication of prematurity resulting from poor lung growth and lung injury. However prior to the description in 1967 of bronchopulmonary dysplasia BPD following ventilator therapy for respiratory distress syndrome WilsonMikity syndrome WMS had been described in very preterm infants on minimal oxygen. Chronic lung disease is defined as oxygen dependency at 36 weeks corrected gestational age. Dysplasia means abnormal changes in the. Chronic Neonatal Lung Disease Bronchopulmonary dysplasia BPD first described in 1967 by Northway Defined as O 2 dependence at 28 days post birth Now termed old BPD Post-surfactant era new BPD arrest at the canalicular phase of lung development Definition changed in 1988 to O 2 dependence at 36 wks Incidence of BPD.
















/GettyImages-91497140-56dfb36a5f9b5854a9f6ca8d.jpg)


















Post a Comment for "Chronic Lung Disease Of Prematurity"